当前位置:首页 → 职业资格 → 教师资格 → 中学英语学科知识与教学能力->设计任务:请阅读下面学生信息和语言素材,设计一节英语阅读课教
设计任务:请阅读下面学生信息和语言素材,设计一节英语阅读课教学方案。
教案没有固定格式.但须包含下列要点:
teaching objectives
teaching contents
key and difficult points
major steps and time allocation
activities and justifications
教学时间:45分钟
学生概况:某城镇普通中学高中二年级学生,班级人数40人。多数学生已经达到《普通高中英语课程标准(实验)》六级水平。学生课堂参与积极性一般。
语言素材:
A Master of Nonverbal Humour
As Victor Hugo once said,"Laughter is the sun that drives winter from the human face", and up to now nobody has been able to do this better than Charlie Chaplin. He brightened the lives of Americans and British through two world wars and the hard years in between. He made people laugh at a time when they felt depressed, so they could feel more content with their lives.
Not that Charlie's own life was easy!He was born in a poor family in 1889. His parents were both poor music hall performers. You may find it astonishing that Charlie was taught to sing as soon as he could speak and dance as soon as he could walk. Such training was common in acting families at this time, especially when the family income was often uncertain. Unfortunately his father died, leaving the family even worse off, so Charlie spent his childhood looking after his sick mother and his brother. By his teens, Charlie had, through his humour, become one of the most popular child actors in England. He could mime and act the fool doing ordinary everyday tasks. No one was ever bored watching him--his subtle acting made everything entertaining.
As time went by, he began making films. He grew more and more popular as his charming character, the little tramp, became known throughout the world. The tramp, a poor, homeless man with a moustache, wore large trousers, worn-out shoes and a small round black hat. He walked around stiffly carrying a walking stick. This character was a social failure but was loved for his optimism and determination to overcome all difficulties. He was the underdog who was kind even when others were unkind to him.
How did the little tramp make a sad situation entertaining? Here is an example from one of his most famous films, The Gold Rush. It is the end of the nineteenth century and gold has just been discovered in Alaska. Like so many others, the little tramp has rushed there in search of gold, but without success. Instead he and another man are hiding in a small hut during a snowstorm with nothing to eat. They are so hungry that the little tries boiling one of his leather shoes for dinner.
Charlie cuts off the leather top of the shoe and shares the shoe with the other fellow. He tries cutting and chewing the bottom of the shoe as if it were the finest steak. Then he picks out the lace of the shoe and eats it as if it were spaghetti. He eats each mouthful with great enjoyment. The acting is so convincing that it makes you believe that it is one of the best meals he has ever tasted.
Charlie Chaplin wrote, directed and produced the films he starred in. In 1972 he was given a special Oscar for his outstanding work in films. He lived in England and the USA but spent his last years in Switzerland, where he was buried in 1977. He is loved and remembered as a great actor who could inspire people with great confidence.
Class Type: Reading class, 1 period
Teaching Contents: This lesson is an introduction about Charlie Chaplin who is a master of nonverbal humour.
Teaching Objectives:
(1) Knowledge objective
Students can listen, read, and then imitate the jokes.
(2) Ability objectives
①Students can develop their reading ability.
② Students can talk about some types of English humour and Chinese humour and then find their differences.
(3) Emotional objective
Students can realize that humour is to let people be optimistic about everything around.
Teaching Key Points:
How to understand and enjoy English humors.
Teaching Difficult Points:
How to understand the differences between English and Chinese in humours.
Teaching Methods:
Using pictures, discussion, reading and imitation
Teaching Aids:
A recorder, a projector and some pictures
Teaching Procedures:
Step 1 Warming up (5 minutes)
Warm up by defining "Humour".
T: What is"Humour" Does anyone of you know anything about Humour Look at the screen and read the definition of Humour from the Internet.
Whose job
This is the story about four people named Everybody, Somebody, Anybody and Nobody. There was an important job to be done, and Everybody was sure that Somebody would do it. Anybody could have done it, but Nobody did it.
Somebody got angry about that because it was Everybody's job. Everybody thought Anybody could do it, but Nobody realized that Everybody wouldn't do it. It ended up that Everybody blamed Somebody When Nobody did what Anybody could have done.
(Justification: Stimulate students' curiosity about English humour and get students involved in talking about this topic.)
Step 2 Pre-reading (10 minutes)
Telling the truth--what do you like to laugh at
Sh I like to laugh at cartoons, for they're lovely and fun.
S2: I like to laugh at fairy tales. They are amusing and interesting.
T: Many years ago there lived an Emperor who was so exceedingly fond of fine new clothes that he spent vast sums of money on dress. To him clothes meant more than anything else in the world. He took no interest in his army,nor did he care to go to the theatre, or to drive about in his state coach, unless it was to display his new clothes. He had different robes for every single hour of the day.
(Justification: Through"Telling the truth--what do you like to laugh at " to stimulate students' curiosity about English humour and prepare them for the reading part.)
Step 3 While-reading (15 minutes)
(1) Reading aloud to the recording
T: Now please listen and read aloud to the recording of the text. Pay attention to the pronunciation of each word
and the pauses twice and you shall read aloud twice, too. I will play the Nonverbal Humour.
(2) Reading and underlining
T: Next you are to read and underline all the useful expressions or collocations in the passage. Copy them to your notebook after class as homework.
(3) Reading to identify the topic sentence of each paragraph
T: Skimming the text and identify the topic sentence of each paragraph. You may find it either at the beginning,the middle or the end of the paragraph.
(4) Reading and transferring information
Read the text again to complete the table.
(5) Reading and understanding difficult sentences
T: As you have read the text several times, you can surely tell which sentences are difficult to understand.
Now put your questions concerning the difficult points to the teacher.
(Justification: Students' reading ability of getting the general ideas and locating the specific information can be trained and improved by skimming and scanning practice.)
Step 4 Post-reading (10 minutes)
The teacher asks students to discuss the most humourous story happened in their live in group. After the discussion the teacher asks them to recommend the most humourous story in each group, and let one student share the story with the whole class.
(Justification: Help the students have a better understanding of the topic of humor.)
Step 5 Summary and Homework (5 minutes)
Summary: To end the lesson by watching a silent humourous movie called"Making a Living" by Charlie Chaplin.
Homework: Do the comprehending exercises in the workbook.
(Justification: Summary and homework is of importance for students to master the knowledge they have learned in class.)
Blackboard Design:
A Master of Nonverbal Humour
What is nonverbal humour
Who is Charlie Chaplin
How does he make a sad situation entertainment
What is the story of The Gold Rush
Facts about Oscar
A brief life history of Charlie Chanlin
Teaching Reflection.
阅读下列材料内容,根据课程标准要求,写出教学内容的教学难点及理由(9分),并设计突破这一难题的教学策略。(17分)
世界上一切事物都包含着既相互对立.又相互统一的两个方面。矛盾就是反映事物内部对立统一关系的哲学范畴。简言之,矛盾就是对立统一。矛盾的对立属性是斗争性,矛盾的统一属性是同一性。它们是矛盾所固有的相反相成的两种基本属性。
矛盾的统一性,是矛盾双方相互吸引,相互联结的属性和趋势,它有两方面的含义:一是矛盾双方相互依赖,一方的存在以另一方的存在为前提,双方共处于一个统一体中;二是矛盾双方相互贯通,即相互渗透,相互包含,在一定条件下相互转化。
矛盾的斗争性,是矛盾双方相互排斥、相互对立的属性。它体现着对立双方相互分离的倾向和趋势。
同一性以差别和对立为前提。没有斗争性,就没有矛盾双方的相互依存和相互贯通,事物就不能存在和发展。斗争性寓于同一性之中,并为同一性所制约,没有同一性,就没有矛盾统一体的存在,事物同样不能存在和发展。矛盾双方既对立又统一,由此推动了事物的运动、变化和发展。
——摘自人民教育出版社普通高中课程标准实验教科书《思想政治必修4——生活与哲学》“矛盾的同一性和斗争性”。
下面是某校高二年级一道学业水平考试的模拟试题及答案要点。
人类离不开海洋,离不开资源丰富的家园,随着人们对海洋资源的肆意开发和狂捕滥捞,近海渔业资源急剧衰竭。浙江象山21名渔老大通过电子邮件和漂流瓶,向联合国和21个滨海国家元首呼吁每年在鱼类产卵和繁殖的高峰季节禁止捕鱼,并向世界渔民发出“蓝色保护志愿者”行动倡议。渔老大的呼吁和倡议,折射出政治、经济、哲学等多方面问题。结合上述材料,以“从渔老大的呼吁看……”为题,分别从《经济生活》《政治生活》《生活与哲学》的角度拟一个课题.并说明理由。
【答案要点】
(1)从渔老大的呼吁看国家宏观调控的必要性。市场调节具有自发性、盲目性和滞后性特点。在近海渔业资源急剧衰竭的背景下,需要国家规定相应的禁渔期以增加渔业资源的发展量。
(2)从渔老大的呼吁看,国家必须增加社会主义法制建设。国家应制定渔业生产法规,以规范渔民与捕捞行为。
(3)从渔老大的呼吁看,必须正确处理尊重客观规律和发挥主观能动性的关系。如果在鱼类产卵和繁殖高峰期捕鱼,势必影响今后的渔业生产。(其他答案,可根据是否与题目具有相关性以及所运用知识的合理性酌情给分)
问题:请根据新课程倡导的评价理念对上述试题及答案作简要评述。(20分)
阅读材料,并回答问题。
材料一:
下列是《文化生活》中“文化创新的源泉和作用”这一教学内容的教学实录片段:

问题:结合该市发展的实际,谈谈社会实践与文化创新的关系。(20分)
传统的思想政治课教学中,教师更注重学生的学习成绩,而忽视对学生情感、态度、价值观的培养。
问题:运用新课程理念,就如何解决这一问题谈谈你的看法。(12分)
材料一:
材料二:
科学发展观的核心是以人为本。要始终把实现好、维护好、发展好最广大人民的根本利益作为党和国家一切工作的出发点和落脚点。科学发展观的基本要求是全面协调可持续,要按照中国特色社会主义事业总体布局,全面推进经济、政治、文化、社会建设。科学发展观的根本方法是统筹兼顾,要统筹城乡发展、区域发展、人与自然和谐发展。
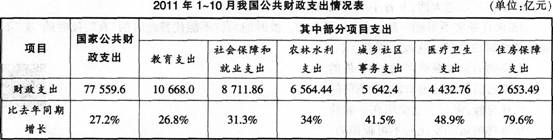
问题:结合上述材料说明我国政府是怎样通过财政支出进一步落实科学发展观的。(12分)
人是法律关系的主体。法律要求尊重每个人的人格和尊严。下面属于民法中人身权的是( )。
①用益物权②名誉权③隐私权④生命健康权
我国合同法规定的承担的合同违约责任方式是( )。
①继续履行②支付违约金③赔偿损失④返还财产
法律是维持社会秩序、调整社会关系的一种行为规范,法律的主要内容( )。
中华文化博大精深,处处闪烁着辩证法思想的光辉。“千里之行,始于足下”“推陈出新,革故鼎新”“因地制宜.因材施教”“金无足赤.人无完人”所蕴含的哲学道理依次是( )。
①矛盾具有特殊性,要具体问题具体分析
②辩证的否定是“扬弃”,是事物发展的环节
③量变是质变的必要准备,质变是量变的必然结果④事物的性质是由主要矛盾的主要方面决定的,看问题要一分为二
求真务实不可能一蹴而就。一劳永逸。彼时的“真”不能代替此时的“真”,彼时的“实”不能代替此时的“实”。这段话强调了( )。