资料:Keeping the Zeal of a Startup as You Scale
There are many reasons that founder-led companies are so good at disrupting industries and making life miserable for slow-moving incumbents. But perhaps the most powerful is that founders create great insurgencies. They ignore established industry rules and boundaries. They create better ways to solve old problems. They disdain anything that blurs their focus on the front line. From top to bottom, they are at war against the industry leaders on behalf of undeserved customers.
Our research on what we call the “founder’s mentality” shows that maintaining a strong insurgent mission is critical to long-term, sustainable growth. But to compete long term, insurgent companies also need to develop scale and scope, which very often dulls their insurgent’s zeal. In many ways, this is because their perspective on the future slowly changes. Insurgents see the days ahead—both long and short term—as ripe with opportunity. They embrace change and chaos. They invest in whatever it takes to innovate new solutions for customers. Incumbents, on the other hand, very often see the future as a threat. As leaders invested heavily in the status quo, innovation and disruption are not good for them. Turbulence erodes profitability; innovation marginalizes their current product offerings. The future is not better.
The companies that find a way to achieve scale without losing their insurgent mission---we call them “Scale Insurgents”--remain acutely alert to this difference in perspective. They actively fight back against the very natural tendency to retreat behind the castle walls to avoid future change and turbulence. Instead, they do what in some companies might seem like heresy---they commit to disrupting their own insurgency. They know that acquiring the benefits of scale requires ruthless focus on a well-defined core business and a commitment to building the systems and processes to support it. But they aren’t wedded to their business model—they are wedded to what will serve their customers best. Rather than erecting defenses against the future, they embrace the notion of limitless horizons—the idea that a company can intelligently extend the boundaries of its core ever outward.
What is main difference between an “insurgent “ company and an “incumbent” company?
本题考查的是细节理解。
【关键词】difference;“insurgent “ company;“incumbent” company
【主题句】第二段Insurgents see the days ahead—both long and short term—as ripe with opportunity. They embrace change and chaos. They invest in whatever it takes to innovate new solutions for customers.(“叛乱企业”把未来(长期和短期)看成充满机遇。他们接受改变和混乱。他们会为了给消费者,把钱投资在寻找新的解决方案上。)Incumbents, on the other hand, very often see the future as a threat. As leaders invested heavily in the status quo, innovation and disruption are not good for them.(另一方面,领导地位的企业通常把未来看成威胁。由于领导者大量投资现状,所以创新和干扰对于他们来说不是好事)
【解析】第3题问“‘叛乱企业’和‘领导地位企业’的主要区别是什么?”。文章第二段谈到了两种企业的不同之处。“叛乱企业”把未来看成充满机遇,接受改变和混乱,会为消费者谋福利。“领导地位企业”把未来看成威胁,不喜欢创新和干扰。综上所述,A选项“‘叛乱企业’把更多的钱投资在未来,然而‘领导地位企业’把钱更多投资在现状。”原文并未说“叛乱企业”会把钱投资到未来,而是说把钱投资在寻找新的解决方案上,故排除A。B选项“和稳定相比,叛乱企业更喜欢混乱。”原文说的是他们接受改变和混乱,并不是说喜欢,该选项过度推理,故排除。C选项“叛乱企业喜欢挑战领导地位企业”,文中并未涉及此选项内容,故排除。D选项“叛乱企业把改变视为机遇,然而领导地位企业更爱稳定。”和原文两种企业的特点一致。
下列关于公司的表述,正确的是()
以下各项列举了我国常见气象灾害与其发生地区的对应关系,其中正确的一项是()
根据电视收视率调査,看体育节目的观众中青年人比中老年人要多。
由此可推断出()
—种海洋蜗牛产生的毒素含有多种蛋白,把其中的一种给老鼠注射后,会使有两星期大或更小的老鼠陷入睡眠状态,而使大一点的老鼠躲藏起来。当老鼠受到突然的严重威胁时,非常小的那些老鼠的反应是呆住,而较大的那些老鼠会逃跑。
以上陈述的事实最有力地支持了以下哪项假说?()
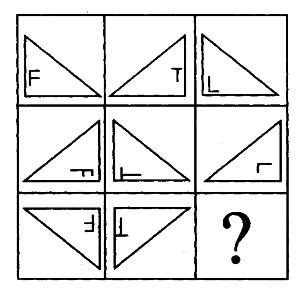
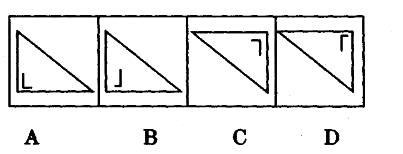
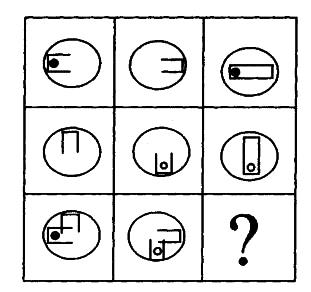
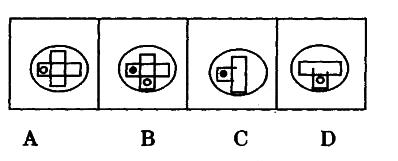
疾病控制中心对某校髙中三个年级的学生进行抽样做视力状况调查,抽样的方法为分层抽样(按比例抽样),若高中一、二、三年级学生人数分别为626、703、780,样本容量为84,则应从离二年级抽样的学生人数为多少?()