资料:Acknowledging that so-called cloud computing will blur the distinctions between computers and networks, about two dozen big information technology companies plan to announce a new standards-setting group for computer networking. The group, to be called the Open Networking Foundation, hopes to help standardize a set of technologies pioneered at Stanford and the University of California, Berkeley, and meant to make small and large networks programmable in much the same way that individual computers are.
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand "express lanes" for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT&T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation's organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know- or care- why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMWare and Yahoo. "This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion." said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues' work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network-the computers-while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
"Orchestrate"in Para.5 probably means______
本题的问题是“第五自然段的‘Orchestrate’可能的含义是______”。根据主题句可知,"Orchestrate"意为“协调”,故选A。
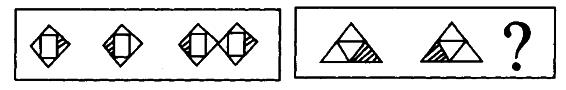
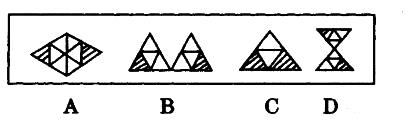
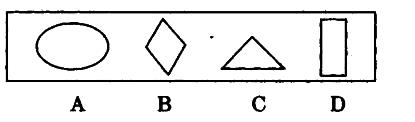
下列关于公司的表述,正确的是()
以下各项列举了我国常见气象灾害与其发生地区的对应关系,其中正确的一项是()
根据电视收视率调査,看体育节目的观众中青年人比中老年人要多。
由此可推断出()
—种海洋蜗牛产生的毒素含有多种蛋白,把其中的一种给老鼠注射后,会使有两星期大或更小的老鼠陷入睡眠状态,而使大一点的老鼠躲藏起来。当老鼠受到突然的严重威胁时,非常小的那些老鼠的反应是呆住,而较大的那些老鼠会逃跑。
以上陈述的事实最有力地支持了以下哪项假说?()
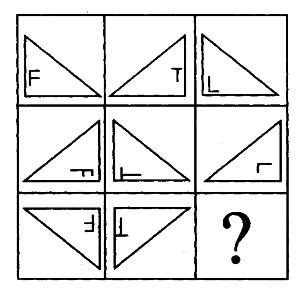
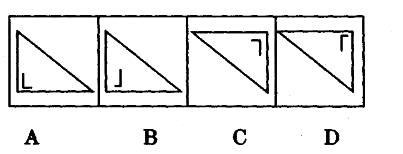
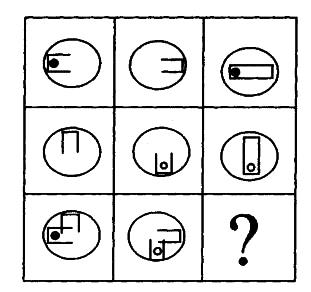
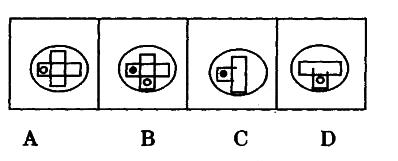
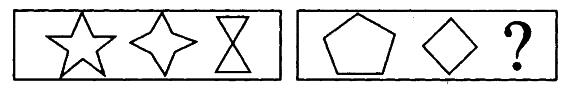
疾病控制中心对某校髙中三个年级的学生进行抽样做视力状况调查,抽样的方法为分层抽样(按比例抽样),若高中一、二、三年级学生人数分别为626、703、780,样本容量为84,则应从离二年级抽样的学生人数为多少?()